
What is angina?
Angina is a pain that comes from the heart. It is common in people over the age of 50. Sometimes it occurs in younger people. It is more common in men than women. This leaflet is about the common type of angina which is caused by narrowing in the coronary arteries of the heart. (Angina is sometimes caused by uncommon disorders of the heart valves or heart muscle.)
Understanding the arteries of the heart
The heart is mainly made of special muscle. The heart pumps blood into arteries (blood vessels) which take the blood to every part of the body. Like any other muscle, the heart muscle needs a good blood supply. The coronary arteries take blood to the heart muscle. The coronary arteries are the first arteries to branch off the aorta. The aorta is the large artery that takes blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the body.
What causes angina?
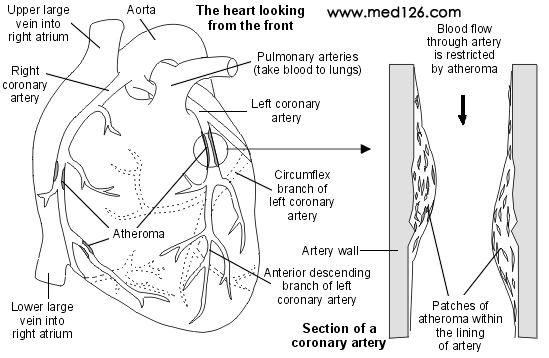
If you have angina, one or more of your coronary arteries is usually narrowed. This causes a reduced blood supply to a part or parts of your heart muscle. The blood supply may be enough when you are resting. However, your heart muscle needs more blood and oxygen when it works harder. For example, when you walk fast or climb stairs, your heart rate increases to deliver the extra blood. If the extra blood that your heart needs during exertion cannot get past the narrowed coronary arteries, the heart 'complains' with pain.
The narrowing of the arteries is caused by atheroma. Atheroma is like fatty patches or 'plaques' that develop within the inside lining of arteries. (This is similar to water pipes that get 'furred up' with scale.) Plaques of atheroma may gradually form over a number of years in one or more places in the coronary arteries. In time, these can become bigger and cause enough narrowing of one or more of the arteries to cause symptoms. (The diagram shows three narrowed sections as an example. However, atheroma can develop in any section of the coronary arteries.)
What are the symptoms of angina?
Typical and common symptoms
The common symptom is a pain, ache or discomfort that you feel across the front of the chest when you exert yourself. For example, when you walk up a hill. You may also, or just, feel the pain in your arms, jaw, neck or stomach. An angina pain does not usually last long. It will usually ease within 10 minutes when you rest, and often within 1-2 minutes if you take some GTN (see below). The pain may also be triggered by other causes of a faster heart rate. For example, when you have a vivid dream or an argument. The pains also tend to develop more easily after meals, or in cold winds.
Less typical symptoms that sometimes occur
Some people have non-typical pains, for example, when bending or eating. If the symptoms are not typical then it is sometimes difficult to tell the difference between angina and other causes of chest pain such as a pulled muscle in the chest, or heartburn. Some people with angina also become breathless when they exert themselves. Occasionally this is the only symptom and there is no pain.
What are the tests for angina?
If you have suspected angina, tests are usually advised.
What can I do to help with angina?
Certain 'risk factors' increase the risk of more atheroma forming which can make angina worse. These are discussed in more detail in another leaflet called 'Preventing Cardiovascular Disease'. Briefly, risk factors that can be modified and may help to prevent angina from getting worse are:醫(yī)學(xué) 全在.線提供quanxiangyun.cn
What are the aims of treatment if you have angina?
The main aims of treatment are:
Treatments that are advised in most cases
Lifestyle measures to reduce 'risk factors'
Discussed above.
GTN (Glyceryl Trinitrate)
This comes as tablets or sprays. You take a dose under your tongue 'as required' when a pain develops. GTN is absorbed quickly into the bloodstream from under the tongue. A dose works to ease the pain within a minute or so. Many people always carry their GTN spray or tablets with them. Some people take a GTN tablet or a spray before any exercise. For example, before climbing stairs. If the first dose does not work, take a second dose after five minutes. (If the pain persists for 15 minutes despite taking GTN, then call an ambulance.)
GTN works by relaxing the blood vessels. This reduces the workload on the heart, and also helps to widen the coronary arteries and increase the flow of blood to the heart muscle.
GTN tablets 'go off' after a few weeks. Therefore, you need a fresh supply of tablets every eight weeks, and return any unused tablets to the pharmacist. You may prefer to use a GTN spray which has a longer shelf life than tablets. A dose of GTN may cause a headache and/or flushing for a short while. This side-effect often improves, or goes, with continued use.
A statin drug to lower your cholesterol level
Cholesterol is a chemical that is made in the liver from fatty foods that you eat. Cholesterol is involved in forming atheroma. As a rule, the higher the blood cholesterol level, the greater the risk of developing atheroma. However, whatever your cholesterol level, a reduction in the level is usually advised if you have angina. Statin drugs lower the blood cholesterol level by blocking an enzyme (chemical) which is needed to make cholesterol in the liver.
There are several brands of statin drugs to chose from. The aim is to reduce your cholesterol level to below 4 mmol/l or by 25% of the original level, whichever gives the greatest reduction.
Aspirin
Aspirin reduces the 'stickiness' of platelets. Platelets are tiny particles in the blood that help the blood to clot after cuts. If lots of platelets become stuck onto a patch of atheroma inside an artery they can form a clot (thrombosis). Therefore, taking aspirin reduces the risk of a heart attack which is caused by a blood clot forming in a coronary artery. The usual dose of aspirin is 75mg daily. This is a lot less than the dose used for pains and headaches. Side-effects are unusual with low dose aspirin. If you have a stomach or duodenal ulcer, or asthma, you may not be able to take aspirin. Options then include to take an additional drug to 'protect the gut', or to use another antiplatelet drug such as clopidogrel. See separate leaflet called 'Aspirin to Prevent Blood Clots - And Other Antiplatelet Drugs' for details.
A beta-blocker drug
Beta-blockers 'block' the action of certain hormones such as adrenaline. These hormones increase the rate and force of the heartbeat, particularly when you exert yourself. Therefore, if you take a beta-blocker it blunts any increase in the rate and force of the heart beat, particularly when you exert yourself. Therefore less oxygen is needed by the heart, and angina pains are prevented, or occur less often. Beta-blockers are also thought to have some protective effect on the heart muscle which may reduce the risk of developing complications.